Gut Dysbiosis
Scientific approach to Combating Digestive Illnesses like IBS and Acid Reflux.
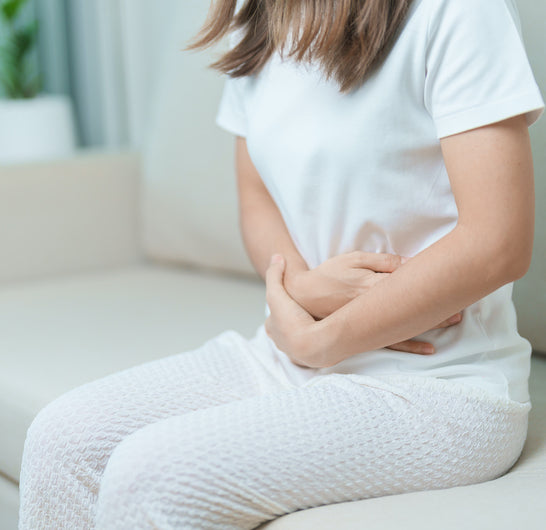
Headaches, brain fog, chronic nasal congestion, bloating, restless legs – yep, those are all signs of histamine intolerance.
Histamine Intolerance
Histamine intolerance affects approximately 3% of the population, and about 80% are women over the age of 40.
Histamine is a naturally occurring chemical that plays a role in our immune and neurological systems. It serves as a neurotransmitter, sending messages from the body to the brain and helping to regulate our stomach acid (Hydrochloric acid or HCL) so we can digest food.
Think of your body like a cup – if the accumulated amount of histamines surpasses the body’s ability to break it down, the cup will overflow.
Alcohol, particularly red wine, is not only rich in histamines but also blocks the DAO enzyme. Without enough DAO to process the histamines in wine, beer, and fermented foods, you'll have an allergic reaction. Symptoms of having a histamine-based alcohol intolerance reaction include a red, hot face.
Causes of Intolerance
Leaky Gut – A leaky gut allows large, undigested food particles to seep into the bloodstream – which signals the immune system to release histamines in response to the threat. Furthermore, intestinal inflammation decreases the ability of the DAO enzyme to break down histamines in the gut, contributing to an overload.
Gut Bacteria – The bacteria in our gut can produce histamines, degrade histamines, or remain neutral. Lactobacillus reuteri (ATCC PTA 6475), Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactobacillus casei, and various strains of E. coli are known to produce histamines. When histamine-producing strains outweigh histamine-degrading strains (i.e., gut dysbiosis), symptoms can occur.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) – In a recent study, 58% of patients with IBS experienced GI symptoms from histamine-releasing foods. IBS patients have more mucosal mast cells (which release histamine) in the rectum, colon, ileum, and jejunum compared to those without IBS.
How can Digbi Help
It can be challenging to know what to eat to improve your health. Digbi Digestive is a program with expert nutritional coaches that guide you every step of the way, teaching you what and how to eat to improve symptoms and quality of life.
A recent study revealed the FODMAP diet “may significantly improve IBS symptoms” by reducing histamines in the gut (as compared to those not on the diet). FODMAP stands for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols, which are short-chain carbohydrates (sugars) that the small intestine absorbs poorly. In general, to ease IBS and SIBO symptoms, it’s essential to avoid high FODMAP foods that aggravate the gut.
That being said, foods that trigger symptoms vary from person to person, so it is important to get your gut and genetic profile analyzed to uncover your trigger foods.
The Digbi Digestive program will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to eliminate your symptoms. You have access to a personalized gut and genetic report, one-on-one feedback, and live coaching. You will also receive access to specific recipes, grocery lists, and ingredients through our app.
Food is our fuel and should never be the cause of pain. Digbi is here to make life easier and help you set up personalized recommendations for your everyday diet to maximize your health outcomes and alleviate any pain linked to your gut microbiome.

Image by Digbi Health
References













Mar 21, 2023 at 07:56AM